- Personalization
The Ultimate Guide to Getting Started with Personalization [in 2024]


The world is full of diverse people with different interests, desires, and motivations.
For this reason, personalization is a major trend in marketing, but it's not always clear how to implement this strategy.
There are a lot of options out there.
Some solutions are complex and expensive to implement, while others provide little value for the price tag.
Your customers will appreciate the personal touch, but implementing this strategy without an expert to guide you can be tough. It's easy to get lost in the weeds and fail before you even begin.
Moreover, most marketers don't have the time or resources to build and manage dozens of different experiences for their website visitors. And even if they do, there are still limitations that prevent them from creating truly personalized experiences like personalizing across channels and devices.
The biggest problem with personalizing your site is scalability. It takes a lot of time and effort to create personalized experiences for each visitor in real-time, which means you can only serve one experience at a time. This leaves most websites with two options: either provide an "average" or "best fit" experience for everyone who visits the site or set up multiple versions of your website (which is expensive).
Neither option works well because consumers don't want average - they want something tailored just for them!
For all of these reasons, we decided to create this guide. In this post, we'll cover everything you need to know about personalization:
What personalization is and is NOT
Benefits of personalization
How to get started with personalization
Personalization types
Personalization and privacy paradox
The future of personalization
What Is Personalization?
According to Cambridge Dictionary, personalization is the process of making something suitable for the needs of a particular person.
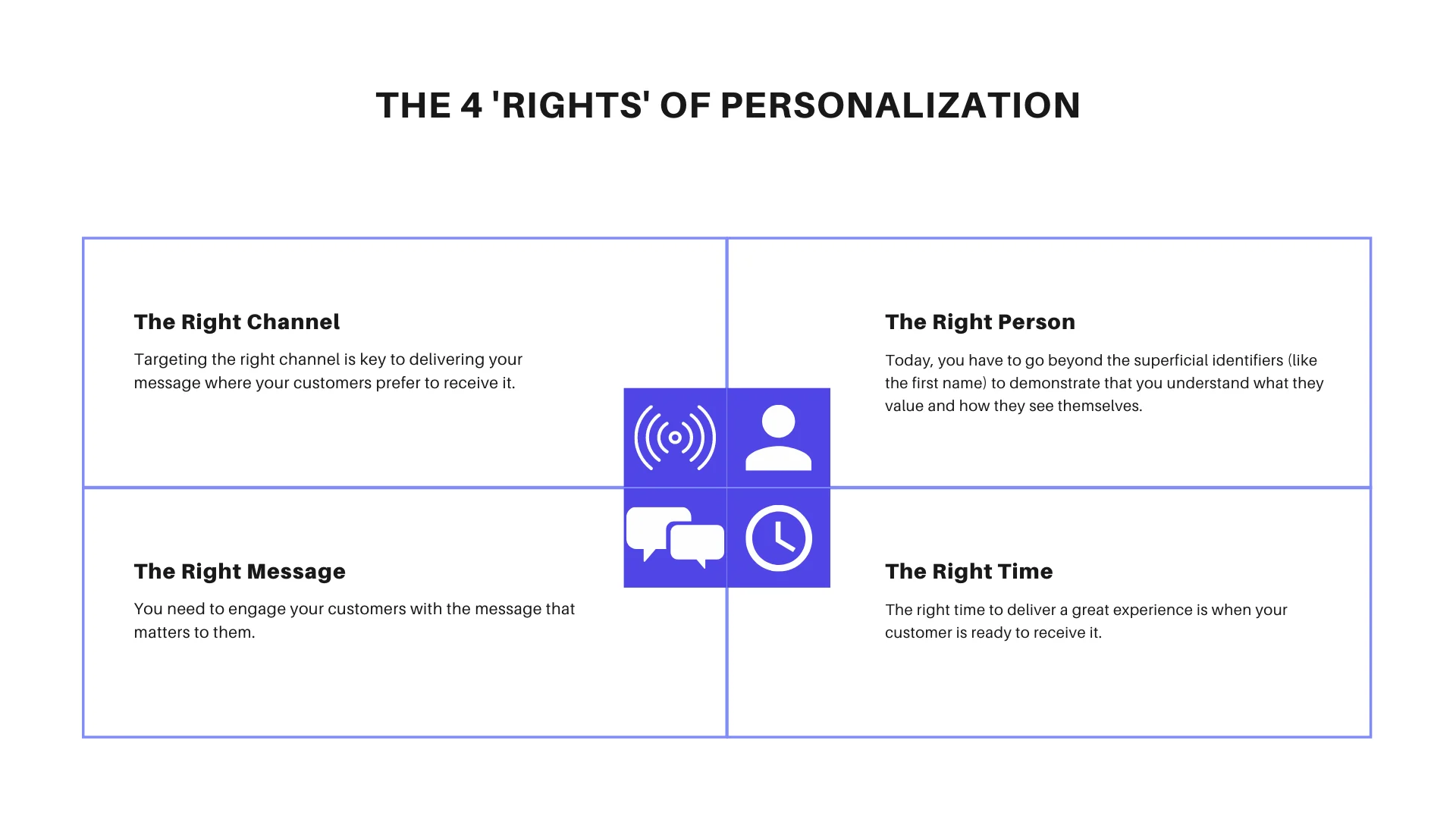
In this definition, we need to pay attention to three things:
process (right time and right channel)
suitable for the needs (right message)
particular person (the right person)
In other words, personalization is a process of continuous efforts to optimize the customer experience to deliver the right message via the right channel to the right person at the right time.
The Right Message → Personalization is not about sending out blanket emails or posts to everyone — it's about adapting your message and approach to what will resonate with each person. Personalization is about tailoring your message to the individual.
The Right Channel → Personalization is about targeting the right channel for a specific customer. It's a way to get customers to engage with your company and allows you to get the most ROI from your marketing efforts.
The Right Person → Personalization is about getting your message in front of the right person. This means understanding everything about them, so you can tailor your product, service, and marketing to fit their needs.
The Right Time → In the end, personalization boils down to identifying the right time for your customers to take action. Personalization can be done at any point in your marketing funnel, whether it's figuring out when to follow up with a lead or when to send a discount code.
What Is Web Personalization
Until here, we understand what personalization is.
Now, the question is: What is website personalization?
It's difficult to make a website stand out in the digital age, but web personalization is one way that companies are trying to capture their customers' attention.
It's no secret that people are drawn to content that is relevant to them.
The idea behind web personalization is that if your site can present information about its products or services in an individualized manner based on what the user has shown interest in before, then they're more likely to stick around and see what else you have for them.
Personalizing your site gives customers a sense of being valued and shows them that you care about their needs.
Web content personalization can be done by tailoring text messages, emails, website pages, social media posts, and ads to meet the customer's preferences. It also means gathering data from visitors to know who they are and when they want a particular piece of content.
What Is Content Personalization?
If you're unfamiliar with the term, content personalization is the process of delivering different content to users based on their individual needs, interests, and preferences.
Content personalization can be done by delivering specific content to different audience segments or by changing the presentation of existing content to match individual visitor preferences.
Content personalization can be done in various ways, including dynamic news feeds, product recommendations based on user behavior, and recommendations based on users' purchase history.
With the increasing amount of web traffic, it is necessary for online business owners to stay ahead of the competition by improving their customer's experience through relevant information.
Content personalization will deliver what your customers want instead of bombarding them with unwanted and irrelevant information.
What Personalization Is NOT
How many times did you receive an email starting with your first name, but the content is literally irrelevant to you?
Let me guess...
So many times, right?
Personalization is something that marketers are always striving for, but most people incredibly misunderstand it.
You might think that it could be as easy as adding your customer's name to a piece of content or email.
But...
This is NOT personalization.
It's not just about putting a name on something or making it seem like you know them better than other people. Personalization is the art of creating content that appeals to individuals based on their interests, background, location, age, and so much more!
The possibilities are endless with personalization and, if done right, can really increase engagement and sales.
Before deep-diving into personalization, firstly, let's understand what personalization is not. Here are some common misconceptions that may be putting you off track:
Personalization Is NOT Only About Tech Stack You Have
Personalization is more than technology.
Yes, technology is very important, but there are other pillars of technology as important as technology.
Personalization is also about
understanding your audience by analyzing the data,
optimizing the user experience,
tailoring the content strategy,
understanding how they interact with your brand, and
knowing where they are spending most of their time online.
Personalization should be approached much like A/B testing. There, the key is constant experimentation and hypothesis-generation based on your findings; these discussions will lead to improvements in goals which can then result in improved behavior for customers.
Personalization Is NOT a Strategy
Yes, personalization is not a strategy.
Personalization is a tool that helps you fuel your plan with creativity so that everything flows together seamlessly towards one goal: accomplishing all those marketing strategies.
To make your personalization efforts more successful, it's important to start defining your goals and strategy.
Defining the goals and strategy will help you find a plan that works for your unique needs - making this whole journey less intimidating!
Personalization Is NOT Being Creepy
Let me repeat it one more time:
Personalization is NOT being creepy.
The goal of personalization is to make your content more relevant to the individual user. If you're trying to market to people based on specific attributes, like gender or location, make sure you're doing so in a way that doesn't make anyone feel weird or uncomfortable.
Moreover, personalization is also not being spammy.
If your efforts are too aggressive, they can turn off potential customers instead of drawing them in. Choose your words carefully, and make sure you're not trying too hard to sound like you know exactly what someone wants.
Why Is Personalization Important?
Personalization is the main factor that will make your website or your business stand out from the crowd. It's not enough to have a good product at a fair price. You must give the customers something they are looking for, something that meets their needs, something that makes them feel special.
Personalization can do just that!
Personalized marketing helps you sell more products, reduce costs and increase profits.
It provides you with insightful data about your clients' preferences to help you improve your services or products. And it helps you build strong relationships with your customers by getting to know them better.
That's why 60% of consumers say they will become repeat buyers after a personalized shopping experience.
Personalized experiences and interactions give you a competitive advantage, and they're only going to become more important. Personalization is a key component of omnichannel marketing and customer experience management.
4 Powerful Benefits of Personalization
The benefits of personalization are clear.
Personalization allows customers to have a more memorable experience when they interact with your brand. It improves conversion rates, promotes loyalty, and encourages repeat purchases.
91% of consumers say they are more likely to shop with brands that provide offers and recommendations that are relevant to them.
83% of consumers are willing to share their data to create a more personalized experience.
80% of companies report seeing an uplift since implementing personalization.
Companies using advanced personalization report a $20 return for every $1 spent.
Here are four major benefits of personalization:
Relevant Product Recommendations
Personalization enables customers to have a more relevant experience when they use your site.
As the e-commerce landscape becomes increasingly competitive, personalization will play an increasingly vital role in how customers interact with brands.
For example, when you visit Amazon and search for a book, you may see suggestions of other books by the same author – and if you've bought other books by the same author – which you might like to buy as well.
Personalization helps make more relevant product recommendations based on what customers have viewed or purchased in the past.
Personalized product recommendations help consumers find what they want, encouraging them to stay on your site longer and purchase more.
Better Understanding of Customer
The main benefit of personalization is that it enables companies to understand their customers better.
With personalization, a company can look at a specific customer and understand how they think and feel in a way that could never be accomplished by tracking trends alone.
This enables companies to create a consistent experience for their customers and create a positive feedback loop, which results in more repeat business.
Tailoring offers and content to the consumer's needs is key to increasing engagement with your product or service. You can do this by analyzing different factors, such as previous purchases, behavioral data, social media interactions, and so on.
Higher Conversion Rates and Customer Lifetime Value
When done well, personalization can increase conversion rates and provide better customer service. When done poorly, it can annoy customers and damage your brand's image.
That's why personalization is so important. When you can tailor your product or service to meet specific needs, it becomes more likely that users will buy. And when they do buy, they're more likely to make repeat purchases after seeing the product or service meet their needs.
That's how personalization can help increase customer lifetime value.
Personalized marketing efforts can increase your customer lifetime value by providing greater convenience, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty, and creating the sense that your organization is more attuned to customer needs.
Personalization can immediately impact your conversion rates and customer lifetime value, so it's worth investing in.
Improved Customer Loyalty
Tailoring your efforts for each individual customer may be difficult. But the more personal you make the experience, the greater the impact will be on customer loyalty.
People like personalization because they believe that it helps them connect with the brand on an emotional level. They like to feel like they're getting something unique, not something mass-produced.
Therefore, personalization can help companies improve customer loyalty and increase customer satisfaction.
When customers feel their needs and preferences are being addressed by a business, they are more likely to spend money, remain loyal to the company, and promote its product to their friends and family.
Common Personalization Challenges (And How to Overcome Them)
Turning personalization into a competitive advantage requires collecting data about customers, storing that data in a database, analyzing it to reveal patterns and trends, and then using the results to deliver personalized customer experiences.
When done well, personalization can drive increased revenues and market share by providing the right products at the right time to the right customers.
But its benefit doesn't come without challenges.
The personalization process must be carefully managed if it's going to deliver greater value than cost. Failure in personalization can result in operational disruption, increased costs, or even reputational damage.
The challenges of personalization include:
privacy
scalability
data collection
incomplete customer profiles
lack of organizational knowledge and capabilities
Content Management and Scalability
Building and deploying personalization at scale takes a lot of time and effort.
One of the most significant challenges to achieving scaled personalization is the time and effort required to create and distribute the massive volumes of personalized content versions suited for various customer segments.
When you have customer segments for multiple geographics, behavioral data, demographics, and psychographics (additionally, technographic data and firmographics for B2B brands), you need the right personalization tool that can be scalable.
On top of that, the development, coordination, and delivery of omnichannel personalization at scale must be made easier for content teams with the right personalization platform in place.
Marketers must have the ability to easily optimize content and message without the need for developer support, and the personalization software should allow for this.
Privacy
The emergence of new technologies provides us with an opportunity to upgrade our lives in previously unimaginable ways.
This has opened up new avenues for businesses, providing personalized customer experiences and targeting their campaigns toward specific audiences.
On the one hand, personalizing the customer experience can help brands connect with their customers on a more human level. However, on the other hand, there are many privacy concerns associated with this practice, resulting in lost trust and even lawsuits.
According to recent research, 69% of consumers say they appreciate personalization, so long as it’s based directly on data they’ve shared with a business.
The bottom line, the privacy concerns related to personalization is mostly about how businesses collect customer data. As long as customers share their information intentionally or give consent to websites to leverage their behavior, there shouldn't be any problem with it.
Data Collection
Personalized content can be great, but you need to know the right information about your users to do it effectively.
The more quality information you have on users and their preferences, the greater your ability will be to serve them relevant content that they will enjoy reading and sharing with others online.
However, if you don't collect enough data or if there's too much noise within what you've collected (i.e., irrelevant data), then personalized content won't work as well as it could—and worse yet—it may actually damage your brand image instead of improving it.
Moreover, your current tech stack needs to work seamlessly to use data from diverse sources to identify and characterize visitors for focused targeting and unified profiles.
Once you have a data stream that syncs seamlessly in real-time, you'll be able to provide the best possible personalized experience for your users.
How to Get Started with Personalization
Up until this section, we've talked about the following:
what personalization is and is not
why personalization is important for businesses
main benefits and common challenges of personalization.
Now, let's make an introduction to how to get started with personalization. In the following sections, we'll dive deep into all the points.
Understanding Fundamentals
Getting started with personalization is simple, even in the face of seemingly overwhelming challenges.
The technology behind personalization has evolved over the last few years, and marketers are now able to deliver more personalized content than ever before.
However, to be able to deliver the right personalization activities, you need to understand the fundamentals of personalization:
First of all, you need to understand that personalization starts with segmentation. Without dividing your customers into segments, how can you create personalized variations for each customer group?
To create customer segments, you need to have customer data. The second backbone of the fundamentals of personalization is having and understanding customer data.
The third point is personalization maturity. Personalization maturity is the model that shows how mature (or advanced) your personalization efforts are. The more data you have, the more hyper-segmentation you can make, and eventually, the more mature your personalization activities will become.
The next point is understanding the personalization types. Usually, when we talk about personalization, we think about web personalization. However, there are different types of personalization such as e-commerce personalization, email personalization, web personalization, PPC personalization, chatbot personalization, app personalization, etc.
The sixth point is understanding the differences and similarities between personalization and customization. Personalization is the process of modifying an experience without any effort from customers. Customization, on the other hand, allows consumers to customize their own experiences by deliberately changing certain elements in order for them to suit themselves better.
Another fundamental point in personalization is understanding the difference between personalization and identification. So far we all understand what personalization is. On the other hand, identification is the act of recognizing and naming someone or something.
The last point in personalization fundamentals is the relationship between personalization and experimentation. We must always keep in mind that personalization is a process. To deliver the best possible customer experience each and every time, we need to create continuous experimentation within the personalization process.
Personalization Starts with Customer Segmentation
Personalization is all about understanding your customers, their interests, and what they value. Without that information, you can't effectively communicate with them in a way that they'll appreciate.
Personalization can be tough when companies have large customer bases, but it gets easier when businesses are able to break down their customer base into smaller groups.
Therefore, an effective way to create personalized experiences is through customer segmentation.
Customer segmentation is the first step in any successful personalization campaign because it allows businesses to see their customers in a new light. By seeing their customers as unique groups with distinct interests, preferences, and behavior patterns, businesses can create relevant customer experiences that help turn visitors into buyers and keep them happy long after the sale.
Segmentation works because it creates a framework for understanding why customers do what they do and how businesses can leverage this information to help customers get what they want out of their experience.
After building customer segments, you can target specific groups of people with custom content and offers based on their interests, behaviors, and needs.
Many organizations fail at personalization because they try to do it all at once for everyone. Instead, start small with one segment and then expand the effort into others until you achieve your desired results.
Here, the personalization maturity model comes into the picture.
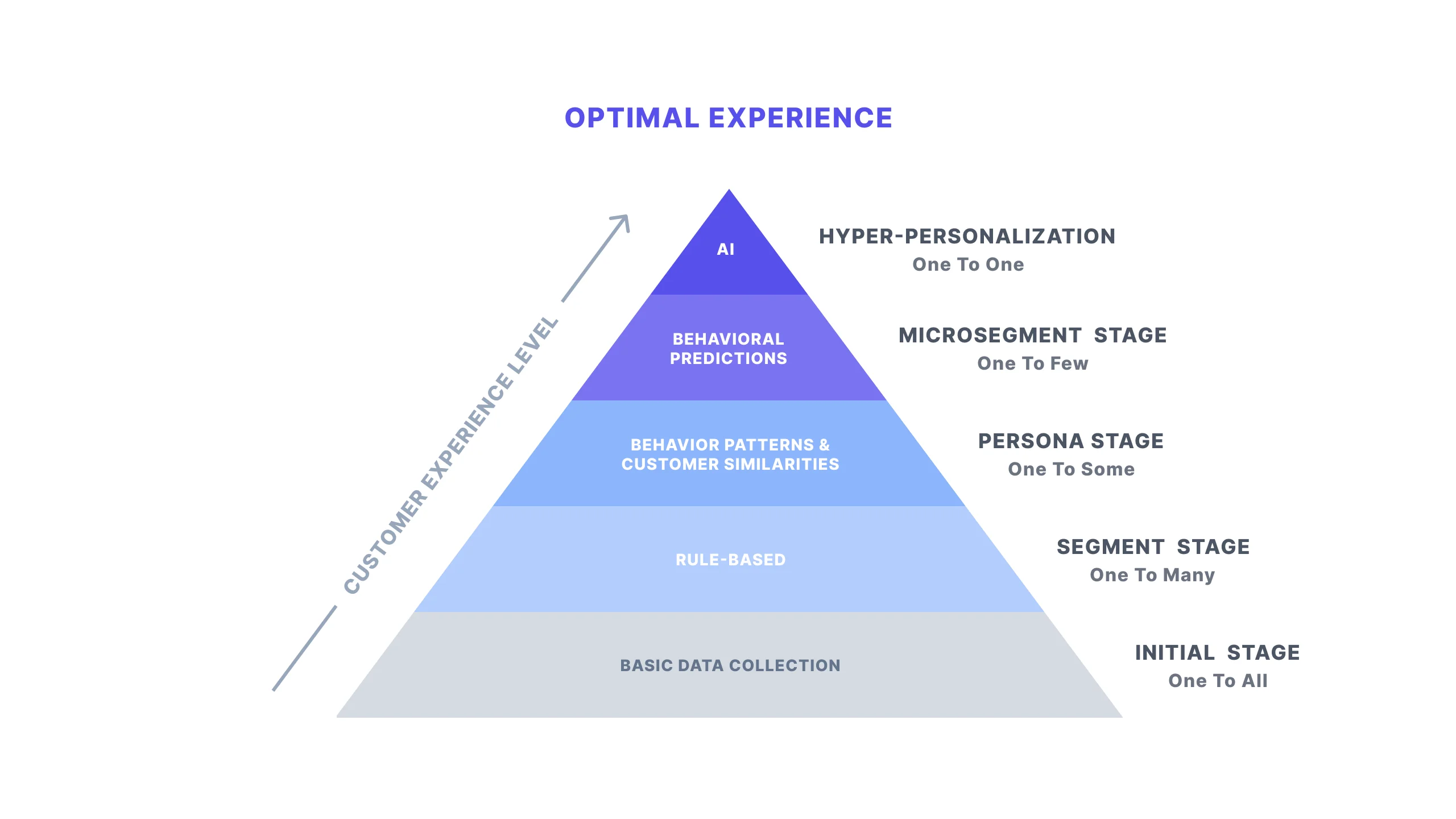
Personalization Maturity Model
The personalization maturity model is a framework that shows you where you stand at your personalization efforts.
One of the most important aspects for determining how personal a company's product or customer experience is to look at what kinds of activities they do in terms of digital products.
In the personalization maturity model, there are five stages:
One-to-All
In other words, the initial stage of personalization.
The initial stage of personalization is basic data collection. The more information you have about your users, the more likely you are to be able to speak to them with intelligence and relevance.
The main purpose of this stage is to collect data about your customers, so you can later target them with content they'll find relevant and engaging.
One-to-Many
The second stage of personalization is the segmentation stage.
In this stage, companies start creating customer segments based on the data they've collected before. If you've collected enough data about your customers, chances are you can identify their needs based on geographic and demographic factors.
One-to-Some
The next stage is the persona stage - where you create deeper customer segments with behavioral patterns.
Until this stage, you have identified your customers. The next step is to segment them into more groups. This helps you to understand how they are similar and also how they are different.
Once you know this, you can provide a more personalized experience for customers.
One-to-Few
The fourth stage in the personalization maturity model is the micro-segmentation stage.
In this stage, the customer segmentation efforts are going even deeper. In addition to geographic, demographic, and behavioral data, you can also use psychographic data.
Moreover, until this stage, it was basically a rule-based personalization. From this stage on, companies start leveraging predictive personalization along with rule-based personalization.
One-for-One
The hyper-personalization stage!
The last stage of personalization. In this stage, brands try to create one-to-one personalized experiences with customers.
In this stage, companies benefit from all the data points across all channels and create one unified profile for every customer.
After that, with the help of artificial intelligence, they try to create the best possible predictive personalization for their customers.
Types of Personalization Channels
Personalization is a process of continuous efforts to optimize the customer experience to deliver the right message via the right channel to the right person at the right time.
When we defined personalization, we talked about four "rights" of personalization:
message
person
time
channel
In this section, we'll dig deeper into the right channel.
There are several different channels that companies can accomplish personalization, such as email, mobile, websites, targeted advertising on social media networks, and even personalized product recommendations on e-commerce sites.
We will discuss the various channels that can be used to create a personalized customer experience, as well as the benefits of using these channels below:
PPC Campaign Personalization
With the ever-increasing competition in marketing, it's no surprise that brands are constantly trying new ways to reach out.
One common way they do this is by annoying their audience with irrelevant content, which will only bore them or turn them off from their product altogether!
Every day we receive a substantial amount of spam and have to suffer through dozens of banner ads when surfing the internet, don't we?
That's why you need to be creative and personal with your PPC campaigns. If your ads don't resonate with the consumer, they are not going to work.
For this reason, you can personalize your PPC campaigns based on:
geographics - such as exact location, climate, population density, language, etc.
demographics - such as age, income level, gender, education level, occupation, etc.
behaviors - such as user status, buyer journey stage, pages visited, benefits sought, loyalty, etc.
psychographics - such as personality, lifestyle, values, interests, etc.
technographic - such as tools and software someone or a company uses
firmographics - such as industry, company size, annual revenue level, etc.
The days of reaching consumers only via keywords are long gone. Marketers may now target their audiences based on demographics, life events, purchasing intent, behavioral patterns, and many other factors.
E-commerce Personalization
E-commerce personalization is the practice of providing personalized experiences on e-commerce sites by dynamically displaying content, product suggestions, and specialized offers based on demographics, past actions, browsing history, purchase behavior, and other personal information.
Personalization is one of the most important aspects of today's e-commerce market when it comes to engaging shoppers and making them repeat customers. 80% of consumers are more likely to make a purchase when brands offer personalized experiences.
This means knowing your customer, and what they like before you even start talking about price points or product assortment so that both parties can have a better experience from beginning to end.
According to recent research, 60% of consumers say they will become repeat buyers after a personalized shopping experience with a retailer. In 2017, this number was 44%.
E-commerce personalization can happen in different ways:
Email Personalization
According to SendPulse, email personalization is an email marketing process that uses subscribers' personal information to produce more targeted emails. It gives individual treatment to the customer and increases email marketing metrics massively.
Although email personalization is about delivering individual treatment to subscribers, there is a massive misunderstanding between identification and personalization when it comes to email personalization activities.
There is a very high number of businesses that say they're doing email personalization. However, in reality, all they do is insert the subscribers' name, {First_Name}, into their email copy.
Well...
This is not an email personalization.
In fact, this is not a personalization at all.
It is identification.
According to Cambridge Dictionary, identification is the act of recognizing and naming someone or something.
Email personalization is:
tailoring the subject line for subscribers
delivering the right content to the right person based on their needs and wants
changing and adapting the email layout for individuals' preferences
In reality, email personalization is tailoring the email experience for each and every subscriber.
When done correctly, email personalization can increase transaction rates 6 times.
Website Personalization
Website personalization is an interactive process of tailoring a website's content to meet its visitors' needs, wants, and desires.
By personalizing the website to suit each visitor, you can increase your chances of making a sale, getting a lead, or even just connecting with your audience on a more personal level.
Web personalization allows marketers to determine what kind of content and offers are most likely to appeal to their visitors. It also allows businesses to direct customers toward products or services they are most likely to be interested in.
This type of personalization can be as simple as changing the banner image on a homepage depending on which country it is being viewed from or as complex as designing a custom product recommendation engine based on previous orders.
A website can be personalized in many ways, including providing targeted marketing messages based on previous browsing history or geographic location data, adjusting page layouts for small screens and mobile devices, or offering different product recommendations based on search queries.
The following are some of the most commonly used ways of website personalization:
Content Personalization → Content personalization refers to dynamically tailoring content elements, such as hero images, page banners, buttons, or any other in-page modules.
Product/Content Recommendations → Showing content or product based on the visitors' behavior, interactions, and previous data.
Notifications → Another type of web personalization is notifications. Again, based on visitors' interactions and behavior, companies can personalize notifications.
Messaging → Messaging refers to any type of text on the website, such as social proofs, reviews, titles, descriptions, etc. Marketers can personalize messaging for their visitors based on different data points.
Menu Personalization → Reorganizing or adjusting the order of the navigation bar depending on each visitor's needs, wants, and preferences.
Search Personalization → Showing search results based on visitors' needs, preferences, and real-time website activity.
Because the consumer journey is no longer linear and encompasses many touchpoints, companies now have even more opportunities to create seamless, relevant experiences via personalization, whether customers are online, in-store, visiting a site through a desktop, reading an email, or accessing a mobile app.
The Similarities and Differences Between Personalization and Customization
When you think of "customization," what comes to your mind?
Nike shoes?
Starbucks drinks?
Your favorite restaurant's menu?
Customization is the process of modifying an experience. Typically, it's used to describe a customer's ability to change something about their experience, like choosing extras on a sandwich or selecting the type of coffee they drink.
Customization is often equated with personalization when it comes to business, but they are actually very different things.
Personalization is a straightforward concept. A company collects information about you and uses it to tailor an experience for you.
Personalization is when a company modifies an experience without any effort from the customer. This can include something as simple as changing the background image on their website or more complex tactics like targeting specific customer segments with different content.
Customization, on the other hand, allows the customer to intentionally modify the experience themselves. It's when a customer is allowed to shape their own experience. They have some level of control over how they interact with your brand. Think about customizing your shoes for comfort or picking out which toppings you want on your pizza.
The key difference between personalization and customization is that personalization requires no thought from the customer while customization does.
A simple way to spot which you're dealing with is to ask yourself whether or not it's possible for a customer to ever experience the product in an un-personalized way. In most cases of personalization, you can't ever escape from being marketed to in some way. If you browse a clothing site and never purchase anything, their items will still be displayed based on your preferences next time you visit.
In contrast, it's possible for a customer to visit a customized site without their experience being personalized at all. A common example would be a custom t-shirt shop that lets you pick your own colors and styles but doesn't use any information about your past purchases or browsing history to market to you.
To sum up, the difference between personalization and customization is how much work customers have to do on their end, but they both aim for more relevant experiences with each interaction you have through your company’s channels.
How Personalization and Experimentation Work Together
Personalization and experimentation are two important tenets of online marketing.
They can help companies understand what works best for their audience, increase website engagement, and drive more conversions. However, they are often seen as separate entities that need to be implemented together in order for them to work correctly.
In reality, though, they are not entirely different concepts at all but rather go hand-in-hand with each other in helping a business reach its goals.
In short, personalization is the process of tailoring a person's experience by delivering specific content or offers to them.
On the other hand, experimentation is the process of generating and analyzing data to improve business decisions.
It's important to recognize that experimentation should be a part of any personalization strategy. It's the difference between making educated guesses and actually testing assumptions.
Personalization isn't just about serving up what we think will be most relevant to users; it's about serving up exactly what they want, need, or are expecting.
As personalization becomes more widespread and integrated into more parts of our lives, it will become increasingly important for companies across industries to get personalization right. And with experimentation as its partner in crime, businesses can achieve exactly that.
The Importance of Customer Data for Personalization
There is no doubt that customer data is the fuel for personalization.
Managing customer data effectively and efficiently is a critical part of creating a personalized digital experience.
Although personalization improves upon the consumer experience, it doesn’t necessarily fuel personalization or deliver direct value to the consumer. Data is what actually allows you to deliver personalized experiences and make relevant associations.
The true value behind personalization comes from leveraging data on the individual level or building a stronger link between your brand and the consumer.
Types of Data Used for Personalization
Data collection has become easier than ever before with the enhancements in technology, but it's also led to an increase in privacy risks that can make or break your business model.
7 out of 10 consumers say they appreciate personalization, so long as it’s based on data they’ve shared with a business directly.
Therefore, it's very important how you collect your customers' data.
There are basically four types of data available by the collection methods:

In addition to dividing data by their collection methods, you can divide each data type into more groups to get a better understanding of the information you have:
Demographic data
Geographic data
Behavioral data
Psychographic data
Firmographic data
Technographic data
etc.

Now, let's look at the four data types by their collection methods:
Zero-Party Data
Coined by Forrester Research, zero-party data is defined as “data that a customer intentionally and proactively shares with a brand, which can include preference center data, purchase intentions, personal context, and how the individual wants the brand to recognize her.”
Zero-party data is privacy-first since it is collected with a user's permission and not by inference.
Moreover, collecting this data does not violate the user's privacy, and it doesn't have the creep factor of third-party data or information inferred from what they do.
This type of data is so valuable because it's not biased.
First-Party Data
First-party data is information about a customer collected directly by a company through its own channels and sources.
Because it is data that an organization has directly obtained via its own channels and sources, first-party data is important and compelling. It is a firm's own data that they do not have to buy or sell to third parties since the client has already willingly provided it throughout their interactions with the company.
However, when acquired without the user's express consent, first-party data raises privacy problems. Companies are obligated by law to get consumer permission before collecting personal information, although these requirements are subject to national rules such as the GDPR and the CCPA.
Second-Party Data
Second-party data is information that you didn't get yourself. It is essentially someone else’s first-party data.
It's sometimes applied between trustworthy companies who agree to share audience data if it's valuable to both of their enterprises.
Third-Party Data
Third-party data is information gathered from several sources, consolidated into a single dataset, packaged, and sold.
Companies that sell third-party data are not usually the same as those who collected the data in the first place. Instead, they collect first-party data from a range of different businesses and bundle it for sale.
Third-party data has come under criticism in the last years, and as a result, Apple and Google have both taken steps against third-party data, with Apple blocking third-party cookies and Google removing the support of third-party cookies from Chrome.
Last but not least, according to recent research, consumers are split about data security. 37% of consumers say they trust businesses to keep their personal data secure and use it responsibly, but another 37% don’t trust online retailers with their personal data.
The Future of Personalization (And How to Get Ready for It)
When you visit a web page, that page is designed to meet your needs.
When you walk into a store, the products on display are ones the retailer thinks you'll like.
When you open your email inbox in the morning, it's full of emails selected by software robots using enough information about you to fill a dozen profiles in your name.
This sort of personalization is everywhere — and it's getting more sophisticated every day — but an important question remains: what will it mean for marketing? And how can companies best prepare for this brave new world?
Personalization is already here, but we've only seen the beginning. In the future, personalization will become an even bigger part of our lives and our businesses.
As people get used to better personalized experiences online and offline, they'll expect that level of service everywhere — from their favorite restaurant down to their local dry cleaner.
In fact, personalized services will be so common that people won't just expect them; they'll demand them!
So how will personalization work in the future? What are the emerging personalization trends? To answer these questions and more, let's take a look at some trends in personalization:
increase in 1:1 experiences with the help of AI and ML
the increasing importance of data privacy and privacy-first personalization
personalizing longer customer journeys
anonymous visitor personalization
omnichannel personalization
Cookieless Personalization
The GDPR has forced marketers to rethink their approach to personalization - specifically, how they can deliver more relevant content without violating the new privacy laws.
The idea of cookieless personalization is becoming increasingly popular because it’s seen as the most GDPR-compliant way to achieve this goal.
So, what is cookieless personalization?
Before explaining cookieless personalization, let's quickly explain what a cookie is.
Cookies are the basic technology used in online advertising to track users from one site to another.
Cookieless personalization does not utilize any information from the consumer’s device — it only utilizes user-generated data or zero-party data.
Overall, the rapidly evolving personalization and privacy paradox will increase the popularity of cookieless personalization.
Omnichannel Personalization and End-to-End Customer Journey Personalization
Personalization is no longer a nice-to-have.
It's become a key differentiator in driving revenue and increasing loyalty.
As consumers have more touchpoints with brands, how we interact with them is changing, too. According to Google, an average person switches between an average of three devices to complete a task. And they use over 10 channels to communicate with businesses.
Consumers connect with brands through multiple devices and at various stages of the buying process – from browsing on mobile to considering on desktop, purchasing on tablets and phones, and engaging digitally after the sale or in stores.
They're doing this as they move seamlessly across digital and physical spaces, expecting that their personalized experiences will follow them where they go.
The customer journey is being increasingly complicated by the blurring of channels and the growing number of touchpoints along these journeys, with companies needing to provide consistent experiences across all these platforms if they want to stay competitive.
In the past, there was a one-way flow of information from companies to consumers. Now we're seeing information both ways.
Although there is a two-way data flow and consumers are using about 3 devices and more than ten channels, only a handful of brands are ready to deliver an optimized, personalized omnichannel customer experience. Recent research found that less than 1 in 4 businesses say they are investing successfully in omnichannel personalization.
Connecting shopping points is a significant potential for the next level of personalization, as expanded partner ecosystems enable companies to create more seamless and consistent customer experiences across all phases of their buyer journeys.
As marketers begin to shift their focus from short-term customer experiences to long-term ones, the effects will be seen almost immediately with increased engagement rates and stronger relationships between brands and consumers.
The more frictionless the experience - both onsite and offsite - the better.
Learn how to deliver unique and personalized customer experiences to increase conversions
