- JAMstack
9 Best JavaScript Frameworks to Use in 2024


JavaScript is a dynamic and interpreted language, it is recognized as the language of the web.
It is a dynamic language that supports a number of programming paradigms, such as imperative, functional, and object-oriented programming. Because of its lightweight design, it is even more suited for the web and is well known for its ability to bring dynamics to static web pages dynamically. However, JavaScript is also used for building server-side applications.
In addition to being used for web development, JavaScript is also used in many other applications, such as desktop applications, mobile apps, and game development.
While JavaScript has been around for more than two decades, it has only recently become a major player in the world of programming languages. Thanks to its versatility and ease of use, JavaScript is quickly becoming one of the most popular languages for both web development and server-side application development.
It has gained traction because JavaScript is one of the many famous and in-demand languages in the IT industry. Due to its widespread, various technologies have been developed around the JavaScript ecosystem, including toolkits, frameworks, libraries, and so on.
This article will introduce to you the best JavaScript frameworks that provide developers with the building blocks to create application software.
What Is a JavaScript Framework?
JavaScript is in itself sufficient to build any web application from scratch. It has all the necessary library it needs to build whatever feature is needed for your application to function just as fine. However, building these features every time you need to build an application can be stressful and time-consuming, so the idea of a template simplifies the building process.
Frameworks are like a set of templates to build certain features of an application. Instead of building the feature from scratch, you can easily build on top of the already existing structure, which helps developers build even more complex applications faster and more efficiently.
Furthermore, a JavaScript framework is a collection of JavaScript libraries to create pre-written code for everyday programmer tasks.
What Is JavaScript Framework Used For?
JavaScript frameworks are used to simplify and accelerate the process of building web applications. They provide developers with pre-written code and a structure to work with, allowing them to create complex applications faster and more efficiently.
Frameworks can handle tasks such as data management, user interface creation, and server-side communication, among others. Overall, JavaScript frameworks make web development easier and more accessible to developers of all levels of expertise.
What Does a JavaScript Framework Do?
Frameworks can be thought of as the actual skeletal or structural foundation of a larger component. This implies that frameworks—including JavaScript frameworks—are the base upon which things are constructed.
JavaScript frameworks are like flexible JavaScript templates that already have predefined functions that can be called upon to speed up the building process of an application. This can be really useful when attempting to design detailed user interfaces or handling massive volumes of data. You can just use the functions already specified in the framework to avoid writing all of the code from scratch. This can help you save a lot of time and work.
Top 9 JavaScript Frameworks
In this section, we will be talking about the different JavaScript frameworks under two categories:
Front End Frameworks
Back End Frameworks
Best Front End JavaScript Frameworks
1. React
React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces and is one of the most popular JavaScript frameworks. It is maintained by Facebook and a community of individual developers.
React can be used as a base in the development of single-page or mobile applications. However, React is concerned with rendering data to the DOM, so creating React apps usually requires additional libraries for state management, routing, and interaction with an API.
React is also known for its high-performance thanks to its use of a virtual DOM, which reduces the time required to re-render the view when the state changes. In addition, React offers support for server-side rendering, which can improve the performance of web applications by allowing data to be fetched before the view is rendered on the client side.
Pros of React.js
Solves the issues of HTML not being a dynamic template with JSX.
Allows for reusing components.
React.js is not opinionated in procedures or approaches to a particular implementation.
React’s functional component looks similar to your JavaScript functions which makes it easy when to learn because you are familiar with it. If you have a proper understanding of JavaScript and HTML templates, understanding JSX should also be easy.
Google's crawlers require javascript in addition to HTML in order to properly read the document and score SEO. With client-side rendering, JavaScript must be downloaded first, which increases load time and causes Google crawlers to skip over documents. However, with server-side rendering, which React.js offers, it is built on the server upon request and sent to the client, which decreases load time and allows Google crawlers to crawl easily, which boosts SEO.
Cons of React.js
JSX can have a steep learning curve.
JSX, hooks, and data binding in React are opinionated.
Key Features of React.js
Virtual DOM: Every React component created is converted to a virtual document object model to adapt all new changes before the actual changes are made in the original DOM.
Cross-Platform: React native is a custom React renderer that uses native components to create user interfaces on mobile devices (iOS and Android) instead of web components.
React Flux: React created an architecture called flux that handles updating the view (React components) on the client-side effectively and follows the one data binding principle.
2. Vue
Vue is a JavaScript framework for building user interfaces and single-page applications. This is another popular JavaScript framework after React. It is also called the progressive JavaScript framework.
It was created by Evan You and is currently maintained by a team of core developers. Vue.js features an incrementally adoptable architecture that focuses on declarative rendering and component composition. It consists of a set of core libraries that are designed to be easy to pick up and use but also extensible and customizable.
The core library is focused on the view layer only and is easy to pick up and integrate with other libraries or existing projects. The one-way data flow model used in Vue.js makes it very straightforward to reason about your application, and its small size makes it highly performant.
Furthermore, Vue.js uses HTML-based template syntax to bind data to the rendered document object model, and it does this by compiling the templates into highly optimized JavaScript code. All Vue format/templates are valid HTML that can be parsed by spec-compliant browsers and HTML parsers.
Pros of Vue.js
Tiny size. Vue.js, if downloaded as a ZIP, only ways 18k as compared to other frameworks.
Simple to learn and is easily adaptable by newbies as they are more familiar with the HTML and JS script, usually in the same file.
Reactivity in Vue3 is achieved by using the Composition API. The Composition API provides an interchangeable way to set up reactivity that doesn't require decorators.
Cons of Vue.js
Small plugin library system.
Vue has a language barrier as some of its largest communities are in China, so Chinese developers create plugins and write documentation in their native language, making it hard for other developers to read.
Too much flexibility in the Vue framework is a disadvantage because of an inconsistent codebase.
Key Features of Vue.js
Composition API: By using the Composition API, you can use redux-like state management within your component without the need for external dependencies. This also results in a more intuitive code structure, making it easier to reason about your application. In addition, the Composition API provides better performance by avoiding the need to create unnecessary re-renderings.
Overall, the Composition API provides a more flexible and performant way to manage reactivity in Vue3.
Single File Component (SFC): Code might be difficult to manage when it is interpolated from three separate files (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript), but with SFC, it can all be written in one file and utilized throughout your application.
Using CSS in a single file component also makes it easier to keep your CSS styles restricted to just that component.
Transition/Animation: Vue.js provides an in-built component called transition that allows you to apply animations to HTML documents when they are added or removed from the document object model dom. The transition component is available in every component across your Vue application.
Computed Properties: This feature is used to update the UI according to reactive data. It is advisable to use the Computed Property when writing any calculated functions that the UI is to be based on since we probably don't want to repeat ourselves if we need to reuse the function elsewhere in our component advised to use Computed Property.
3. Ember.js
Ember is a component-based JavaScript framework that was created in 2011 by Yehuda Katz. Ember had its stable release in 2016. Ember's goal is to make web development more productive and enjoyable by providing a comprehensive toolset that covers the entire development process by providing a router, view layer, and data management library.
Ember uses its FastBoot technology for server-side rendering for Ember apps. Using FastBoot, you can serve rendered HTML pages to browsers and other clients without requiring them to download JavaScript assets first.
Everything in Ember can be tagged as a service or a component, which is readily available all over your Ember app and can be called anytime. This means that you can have a long file of HTML template and decide to break it into small bits, and these bits can be placed in the app/component folder, which makes that bit of your template a component and can be called as a custom HTML tag.
Furthermore, Ember’s routing system has tight integration with the browser’s URL. Ember uses its router to map URLs to a route handler. The router can match the current URL to other routes which are used to load data, display templates, and show the app state.
Pros of Ember.js
Convention over configuration helps reduce the number of choices to be made and, in turn, reduces error.
Most Ember apps have the same structure everywhere, which makes understanding a codebase easy within a short time.
Ember has a dev tool built into the ember-CLI that can be used to x-ray or debug your Ember app.
Cons of Ember.js
It’s very opinionated.
Learning difficulty is on the high side because things change fast, and when you try to find solutions, more materials are covered in the older solutions than the new pattern.
Low popularity.
Key Features of Ember.js
Components: You can decide to break large junk of code into smaller units which helps reduce the complexity of code and makes it easier to maintain.
Routing: What sets Ember apart is the introduction of routing, which is used to manage URLs.
Service: You can create a third-party service in your Ember app that is available throughout the life cycle of your Ember application, and it can be generated using the ember-CLI.
Ember Data Models: Different applications have different models based on the problems they want to solve. An application might have a checkout or cart model, but if the user refreshes his or her application, we expect the data to be persistent and not lost. We can achieve this persistent data using the Ember Data Model.
4. Next.js
Next.js is a free and open-source React front-end framework created by Vercel. It is used to build user interfaces and static websites. The framework is also capable of creating server-side rendering and universal applications.
Next.js uses JavaScript and React components to create the UI. Next.js is influenced by React Router, Webpack, Node ecosystem, and community libraries. The feature that sets Next.js apart from other frameworks is its ability to automatically generate pages based on the file system structure of the project. For example, if there is a _posts folder in the root directory, Next.js will generate a page for each markdown file inside it.
This feature allows for a faster development process, eliminating the need to create pages for each piece of content manually. Another unique feature of Next.js is its incremental static generation which allows for statically generated pages to be updated incrementally as new content is added or changed.
Pros of Next.js
Build static websites fast with dynamic functionalities.
Next.js stands out for SEO because it offers server-side rendering and the building of static websites.
Good community support.
Fast time to market: With pre-made components, you may enter the market more quickly while saving time and money. These components can assist your teams in swiftly enhancing and approving iterations.
Responsive design: Become flexible and responsive to ensure that your designs look fantastic on all devices, regardless of screen size.
Cons of Next.js
Poor plugin system.
Routing is constrained except for an option with Node for dynamic routing.
When an application contains several pages, the build time is really significant.
Key Features of Next.js
Pages: You can create pages and navigate them on the browser using the file routing system in Next. To use the file routing system create your pages in the pages folder pages/first-post.js. The initial route is usually associated with the pages/index.js file.
Image Optimization: The image component is an extension of the HTML element img. It’s improved for the modern web. The improved image component can help resize images on any device and loads the image only when it is in the viewport.
TypeScript Support: Next.js provides an integrated TypeScript experience in both existing and new projects. While creating new projects, you do not need any configurations to set up TypeScript.
Supported Browsers: All modern browsers are supported by Next.js and IE11 (Internet Explorer 11) inclusive with no necessary design. Polyfills are injected for IE11 compatibility and are only loaded when needed but are usually disposed of during production when not needed in browsers that have IE11 compatibility to avoid duplicates.
Data Fetching: Next.js features two types of rendering: static generation and server-side rendering.
Static Generation: Here, the HTML page is generated at build time, cached in a CDN, and is already built whenever requested.
Server-Side Rendering: In this case, dynamic content pages are generated and served to the client from the server and rendered on every request.
Layout: If you have to need your Navbar and your Footer on every page of your app, you do not need to add the Navbar and Footer component on every page. Next allows you to deconstruct a page into a series of components, wrapping the Navbar and Footer components on every page.
5. Angular
Angular.js is a powerful JavaScript-based web development framework. It has been designed to make web development more efficient and easy to use. Angular.js is based on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which makes it easy to develop dynamic web applications. It also provides many features that make web development more efficient, such as data binding, dependency injection, and template systems. In addition, Angular.js is highly modular, making it easy to create custom modules and libraries.
Angular.js allows you to extend HTML vocabulary to create interactivity in your angular application using directives, making the code more readable, expressive, and easy to develop. Additionally, Angular.js includes a number of built-in features such as data binding and dependency injection, which further simplify the development process.
Pros of Angular
Logic is separated from the view using the MVC pattern, which is most familiar amongst developers.
Angular is modular, which means when building an application, components, services, pipelines, and so on can be stored in an Angular modularity system called
NgModules, and these modules can be exported and used to create even more complex applications.Reuse of components or using services might need to depend on other services sharing their instances with other components in other components. This is where dependency injection is needed.
Easy DOM manipulation. Since Angular works directly with the DOM, changes take effect immediately, and a virtual Dom is not required.
Two-way data binding.
Angular is very testable. Testing hooks are made available by the Testability service and can be accessed from the browser.
Cons of Angular
Understanding Angular takes time because of the intricate web of modules, coding languages, integrations, and customization options.
Angular is rather complex compared to React and other frameworks.
Key Features of Angular
Data Binding: This is just synchronization between the model and the view. When there is a change in the view, the model is updated; when there is a change in the model, the view is updated automatically at all times.
Directives: Angular allows you to extend HTML with built-in attributes with the ng prefix. These attributes are used to add interactivity/functionality to your Angular app.
Dependency Injection (DI): A small part of your app can require HTTP service to make backend calls, with the DI system, you can deliver those service to the parts of the application that needs it.
Templates: Each template in Angular is a chunk of HTML code and a fragment of the application UI. It is regular HTML but with more functionality.
Best Back End JavaScript Frameworks
6. Node.js
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime environment that is used to develop server-side applications. It is based on the V8 JavaScript engine used in the Google Chrome web browser. Node.js was created by Ryan Dahl in 2009 and has since become one of the most popular JavaScript platforms used today.
Node.js applications are written in JavaScript and run on the Node.js runtime, which allows them to be executed on any platform that supports Node.js. Node.js applications are typically event-driven and single-threaded, making them efficient and scalable. Additionally, the Node Package Manager (NPM) provides a way to install and manage dependencies for Node.js projects easily. overall, Node.js is a powerful platform that makes it easy to develop fast and scalable web applications.
Pros of Node.js
High performance because it uses the uses V8 JavaScript Runtime engine.
Easy to Learn: Node is pure JavaScript. If you are already familiar with JavaScript, you don’t put so much effort into learning Node.
Good community.
Handling Concurrent Request: Node can manage thousands of concurrent connections on a single process with very little overhead.
Cons of Node.js
Too much reliance on callbacks.
Asynchronous programming makes it difficult to maintain code.
Developers depend on third-party libraries to complete certain tasks.
Processes one request at a time.
Key Features of Node.js
Event Driven/Asynchronous: One of the reasons behind the Node.js speed is that once a Node.js server is started, it initializes variables and functions and listens to any occurrence of events. This makes Node.js handle different connections concurrently without having to block the execution of other code in the server using callbacks.
Single-Threaded: Node.js uses event looping and single-threaded models. The event architecture makes the Node.js server respond asynchronously, making the server highly scalable compared to other servers.
No Buffering: Node.js applications do not buffer data; they out data in chunks.
Very Fast: Node.js is built on Chrome V8 JavaScript engine; it is fast in code execution.
7. Backbone.js
Backbone.js is a JavaScript library that provides Model-View-Presenter (MVP) architecture and synchronization for web applications.
Backbone.js is based on the Model View Controller (MVC) design pattern. The library supports seven components: Models, Views, Collections, Routers, Events, Sync, and Options. Backbone.js also provides an asynchronous communication layer that allows the application to communicate with a backend service.
Backbone.js is specifically designed for Single Page Applications (SPAs). A Single Page Application is a web application that loads all of the resources required to use the application on the initial page load. This eliminates the need to reload the page when navigating to different sections of the application.
Backbone.js is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries for building SPAs. It is used by companies such as Airbnb, Walmart, and Tumblr.
Pros of Backbone.js
Backbone.js is lightweight. It is 20kB minified.
Backbone.js is flexible and easy to use. You can get started within minutes.
You can combine and match the components that work best for your application's requirements, and BackboneJS will get along with any improvements you decide to make, allowing you to adapt it to your project's requirements.
Good documentation.
Cons of Backbone.js
It’s opinionated about RESTful API.
Writing unit tests can be difficult because you probably need to write long lines of mock code to write unit tests.
Backbone.js creates empty and redundant
divelements for its view.
Key Features of Backbone.js
JavaScript Functions: By utilizing JavaScript functions, Backbone.js makes it much simpler to design frontends and applications.
Extensions: Backbone.js is an open-source project and contains over a hundred extensions.
Core Libraries: Backbone.js is meant to be used with jQuery and Underscore.js as backend technologies.
Models and View: It serves as the framework for your project and aids in the organization of your code by separating the logic from the UI, thereby leaving you with a maintainable codebase.
Collections: By managing the loading and storing of new models to the server and handling utility functions for performing aggregations or computations against a list of models, a Collection assists you in managing a set of related models.
8. Meteor.js
Meteor.js is a JavaScript-based platform for developing web applications. It’s open source and supports various programming paradigms, including object-oriented, functional, and event-driven programming. Meteor.js is based on the Node.js framework and uses an asynchronous programming model.
Meteor.js also includes a number of built-in libraries for everyday tasks, such as networking, data manipulation, and UI rendering. In addition, Meteor.js provides a command-line tool for creating and deploying web applications.
Meteor.js is popular for developing real-time web applications, such as chat clients and step-by-step tutorials. It is also well suited for developing cross-platform applications that can be deployed on multiple devices.
Pros of Meteor.js
Real-time change on the server.
Running several copies behind a load balancer makes it simple to scale horizontally.
Build apps for both web and mobile apps.
Cons of Meteor.js
A lot of what is going on underneath is not properly explained.
Meteor.js is monolithic in as it is used to build for different platforms and uses one data source.
When distinct modules have divergent resource needs, scaling monolithic applications can be difficult.
Key Features of Meteor.js
Cross-Platform Development: Meteor offers a platform to develop applications across the web, Android, iOS, and the desktop.
Unicode Base: Use one codebase to develop the same app for other platforms.
Packages: Has a good number of packages to install and use.
Meteor Galaxy: Cloud platform for deploying meteor apps.
9. Express.js
Express.js is a web application framework for Node.js, released as free and open-source software under the MIT License. It is designed for building web applications and APIs.
It has been called the de facto standard server framework for Node.js. Express.js' main features are its soft dependencies, plugin system, high performance, easy routing, and lack of callback Hell.
Express.js brought the component-based design to Node.js web applications! This helps developers reuse middleware and makes it easier to scale an Express.js project as your team members grow.
Additionally, Express.js v4 now comes with built-in middleware for handling AJAX requests from the client side, making it even easier to get started without having to worry about 3rd party libraries. Express.js is a great tool for quickly building out web applications and APIs in Node.js.
Pros of Using Express.js
Easy to learn and implement. Getting started with it will be simple if you are already familiar with JavaScript and Backend Architecture.
Because Express.js is a basic framework, middleware packages have been developed by the Express development team to address various development issues.
JavaScript may be used on both the front end and the back end thanks to the Express.js framework. It offers JavaScript programmers the chance to learn all aspects of the language. One person can now manage both the presentation layer and the data access layer, making the development process considerably quicker and simpler.
Includes a variety of middleware modules that you can use to add to request and response operations.
Cons of Using Express.js
Error messages are not descriptive.
It has an unbalanced API.
Might have security issues.
Key Features of Express.js
Offers simple client routing requests.
Works as a middleware.
The Bottom Line
In terms of web development, JavaScript is still the most popular language. But each different JavaScript framework has its own applications, benefits, and drawbacks. Therefore, keep that in mind while you consider your options.
Before selecting a framework for your application, carefully review your project's needs. Each framework has special capabilities that you could need while developing. Along with the features, take into account the difficulty, learning curve, documentation for compatibility, and community assistance.
We hope that our recommended list of JavaScript frameworks will assist you in selecting the best one for your project. Visit our article on the top JavaScript courses if you want to learn the language.
This concludes our list of JavaScript frameworks. Which one do you prefer?
Download the best JavaScript frameworks guide to answer the 'which JavaScript framework to use for your next project?'
Frequently Asked Questions About JavaScript Frameworks
Which Is the Most Popular JavaScript Framework?
According to the JAMstack community survey of 2022, React is currently the most popular JavaScript framework.
This comes as no surprise, as React has been consistently popular among developers for several years. React's popularity can be attributed to its ease of use, flexibility, and performance. Its component-based architecture makes it simpler to build large-scale applications, and its virtual DOM allows for efficient updates and rendering. Additionally, React has a large and active community, which provides a wealth of resources and support for developers.
Overall, React's popularity is a testament to its usefulness and effectiveness in building modern web applications.
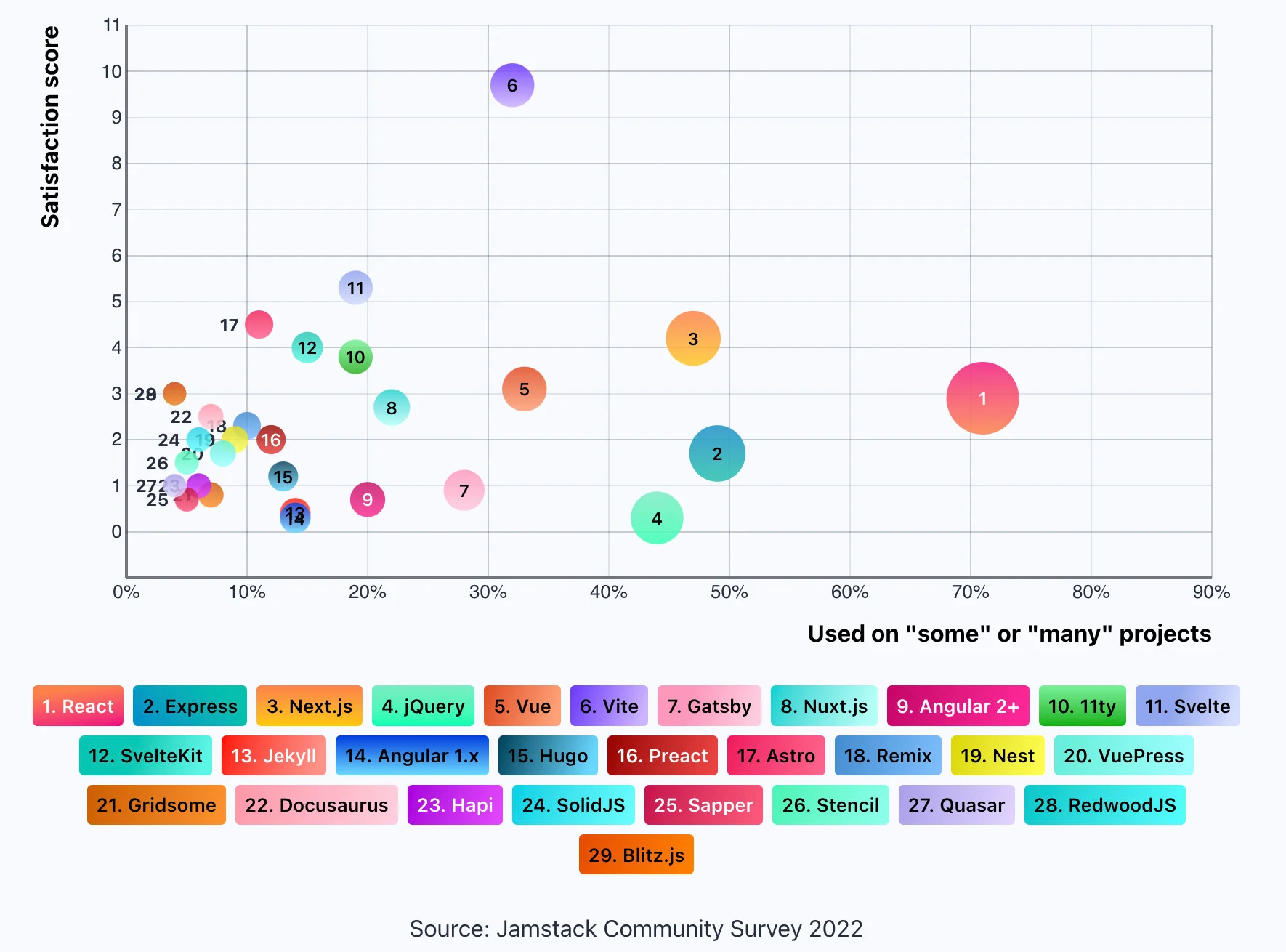
What Is the Most Used JavaScript Framework?
According to the annual JAMstack community survey conducted in 2022, React has emerged as the most popular JavaScript framework. This comes as no surprise, as React has been consistently popular among developers for several years now.
The popularity of React can be attributed to its ease of use, flexibility, and performance. Its component-based architecture makes it simpler to build large-scale applications, and its virtual DOM allows for efficient updates and rendering. Additionally, React has a large and active community, which provides a wealth of resources and support for developers.
Overall, React's popularity is a testament to its usefulness and effectiveness in building modern web applications. If you're considering choosing a JavaScript framework for your next project, React is definitely one to consider.
Which JavasScript Framework Is Best for Web Development?
When it comes to choosing the best JavaScript framework for web development, it ultimately depends on your project's requirements and your personal preferences. However, some of the most popular and widely used JavaScript frameworks for web development include:
React: A powerful and flexible framework for building user interfaces. It uses a component-based architecture to create reusable UI elements and has a large and active community.
Angular: A comprehensive framework that provides a lot of features out of the box, including data binding, dependency injection, and more. It uses the MVC architecture and is highly modular, making it easy to create custom modules and libraries.
Vue.js: A lightweight and easy-to-learn framework that focuses on simplicity and ease of use. It uses a reactive data binding system and has a growing community.
Ember.js: A framework that provides a lot of built-in features and conventions, making it easy to get started and build complex applications. It uses the MVC architecture and has a strong focus on developer productivity.
Backbone.js: A lightweight and flexible framework that provides a lot of freedom and control to developers. It uses the MVP architecture and is highly customizable.
Ultimately, the best JavaScript framework for web development depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider factors such as the size and complexity of your project, your development team's experience and expertise, and the level of community support and resources available for each framework.
How Many JavaScript Frameworks Are There?
It's difficult to give an exact number, as new JavaScript frameworks are constantly being developed and released. However, there are currently more than hundreds of JavaScript frameworks available, ranging from small and simple libraries to comprehensive and complex frameworks. Some of the most popular and widely used JavaScript frameworks include React, Angular, Vue.js, Ember.js, and Backbone.js. Ultimately, the best framework for your project depends on your specific needs and preferences.
Which Are the Best JavaScript Frameworks to Learn?
Based on popularity and usage, some of the best JavaScript frameworks to learn are:
React: According to the JAMstack community survey of 2022, React is currently the most popular JavaScript framework. It is widely used for building user interfaces and has a large and active community.
Angular: Angular is a comprehensive framework that provides a lot of features out of the box, including data binding, dependency injection, and more. It is highly modular and is used by many large enterprises.
Vue.js: Vue.js is a lightweight and easy-to-learn framework that focuses on simplicity and ease of use. It has been gaining popularity in recent years and has a growing community.
Ember.js: Ember.js provides a lot of built-in features and conventions, making it easy to get started and build complex applications. It has a strong focus on developer productivity.
Node.js: While not strictly a front-end framework, Node.js is a popular choice for server-side JavaScript development. It is based on the V8 JavaScript engine used in the Google Chrome browser and is widely used for building scalable and efficient web applications.
Ultimately, the best framework to learn depends on your specific needs and preferences, as well as the requirements of your project. Consider factors such as the size and complexity of your project, your development team's experience and expertise, and the level of community support and resources available for each framework.
How to Choose a JavaScript Framework?
When it comes to choosing a JavaScript framework, there are several factors to consider. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
Project Requirements: Consider the requirements of your project, such as the size and complexity of the application, the need for real-time functionality, and the target audience.
Developer Experience: Consider the experience and expertise of your development team. Choose a framework that aligns with their skill set and knowledge.
Community Support: Look for a framework with an active community of developers. This can provide you with access to helpful resources, libraries, and tools.
Scalability: Choose a framework that can scale with your project. This can help you avoid the need to switch to a new framework later on.
Maintenance: Consider the maintenance requirements of the framework. Choose a framework that is regularly updated and has good documentation.
Ease of Use: Choose a framework that is easy to use and understand. This can help you save time and effort during development.
Ultimately, the best JavaScript framework for your project depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider these factors when making your choice, and don't be afraid to try different frameworks to see which one works best for you.
Which JS Framework Is Best in 2024?
In 2024, the landscape of JavaScript frameworks continues to be diverse and dynamic, with various options catering to different needs, from building interactive user interfaces to developing server-side applications. The choice of the "best" JavaScript framework largely depends on the specific requirements of the project, the development team's familiarity with the framework, and the community and ecosystem support. Here is an overview based on the latest insights:
React.js remains a dominant player, highly favored for its component-based architecture, making it incredibly efficient for developing large-scale applications with data that changes over time.
Angular, being one of the most actively developed frameworks at the beginning of 2024, offers a comprehensive solution with a robust set of features for building complex client-side applications.
Vue.js is celebrated for its progressive nature, allowing developers to adopt it incrementally. Its simplicity and flexibility make it a popular choice for both small projects and large-scale applications.
Svelte stands out by shifting much of the work to compile time, producing highly optimized vanilla JavaScript at build time, which enhances performance and leads to faster page loads.
Next.js is gaining traction for its server-side rendering capabilities and static site generation, making it an excellent choice for SEO-focused projects and applications requiring fast load times.
Node.js and Express.js continue to be the go-to solutions for building scalable server-side applications and APIs, thanks to their non-blocking, event-driven architecture.
Emerging frameworks like TezJS and Qwik are also gaining attention for their innovative approaches to enhancing performance and developer experience.
Ultimately, the "best" framework is subjective and varies depending on the project's specific needs, the development team's expertise, and the desired outcome of the application. It's advisable to evaluate the features, community support, and long-term viability of each framework before making a decision.
Download the best JavaScript frameworks guide to answer the 'which JavaScript framework to use for your next project?'